Cross Flow Heat Exchanger Equations
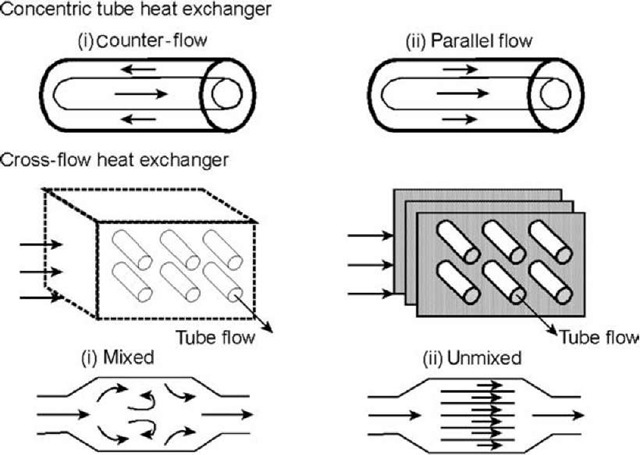
Effective incorporation of heat exchanger networks will minimize the use of utilities minimize the number of heat exchangers and minimize costs associated with the design. Parallel and Counter-Flow Designs Parallel and Counter Flow heat exchanger Designs.
Cross Flow Heat Exchangers All Practical Guides You Should Know
Heat transfer rate in the exchanger is represented by.

. The equations for determining the amount of energy saved Btu in a year use the cfm HDD the efficiency rating of the heat exchanger EF and a constant for the specific heat and specific weight of air 2592. Control volume analysis of mass momentum and energy pipe and duct flow dimensional analysis steady and unsteady heat conduction internal convection and application of boundary conditions and simple heat exchanger design. This lets us find the most appropriate writer for any type of assignment.
An illustration of working of a cross flow heat exchanger Reference. The airstreams flow at right angles to each other. The heat exchange duty a llows calculation of the log mean.
The thermodynamic free energy is the amount of work that a thermodynamic system can perform. Or perpendicular to each other - cross flow. The pinch point divides the temperature range into two regions.
The basic component of a heat exchanger can be viewed as a tube with one fluid running through it and another fluid flowing by on the outside. If the curves cross this means that heat transfer will switch direction which is physically impossible the best that can happen is for both streams to reach the same temperature. Determination of the α values according to the equations for the convective.
In case of cross flow heat exchanger measure the air velocity at the inlet to the blower with the help of a digital anemometer. Heat Exchangers Transfer of heat is usually accomplished by means of a device known as a heat exchanger. We will guide you on how to place your essay help proofreading and editing your draft fixing the grammar spelling or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply.
2 The required relative heat transfer surface area as a function of the ratio of the temperature rise or drop in the fluid stream having the greater change in temperature to the difference in. We now have two equations and and two unknowns and. Heat exchanger networks are designed through insightful use of pinch analysis.
In the opposite direction - counter-current flow. In computers heat sinks are used to cool CPUs GPUs and some chipsets and. The heat transfer rate may be considered as a current flow and the combination of thermal conductivity thickness of material and area as a resistance to this flowThe temperature difference is the potential or driving function for the heat flow resulting in the Fourier equation.
The basic relationships for these three processes can be expressed using Equations 2-5 and 2-9. Number of Transfer Units NTU. A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluidHeat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes.
It is possible to compare heat transfer to current flow in electrical circuits. Here F 1 is interpreted as a geometric correction factor that when applied to the LMTD Log Mean Temperature Difference of a counter flow heat exchanger provides the effective temperature difference of the heat exchanger under consideration. Note down the pressure of steam from pressure gauge on steam header.
Cross-flow heat exchangers also use flat plates. The 50 ethylene glycol at a rate of 047 kgs enters at 90C. A heat sink also commonly spelled heatsink is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium often air or a liquid coolant where it is dissipated away from the device thereby allowing regulation of the devices temperature.
Each expression belongs to a specific class of exchangers. Heat transfer is the energy exchanged between materials solidliquidgas as a result of a temperature difference. Upper tube sheet.
Parallel Flow Heat Exchanger Efficiency of heat exchanger with the parallel arrangement is. Counter-Flow Heat Exchanger For Cross-Flow and Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchangers. Topics covered include basic methods for single-phase pressure drop and heat transfer condensation boiling two-phase flow.
Our global writing staff includes experienced ENL ESL academic writers in a variety of disciplines. Varepsilon frac1-mathrmexp -NTUleft1C_rright 1C_r Counter Flow Heat Exchanger. Q h 1 A 1 T o 1-2 DT o can be expressed as the sum of the DT of the three individual processes.
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic potential designated by the letter H that is the sum of the internal energy of the system U plus the product of pressure. Example 52 Miniature Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchanger A miniature shell-and-tube heat exchanger is designed to cool engine oil in an engine with the engine coolant 50 ethylene glycol. The Design Manual is the comprehensive reference for HTRIs thermal design recommendations for all types of heat exchangers.
In case of plate type or shell tube type heat exchanger note the water flow rate to the heat exchanger from the digital display. A Counter current flow b One shell-pass two tube-pass c Two shell-passes four tube-passes. Course emphasizes internal flow and modes of heat transfer.
It summarizes calculation methods in HTRI software provides design recommendations and offers practical design tips. Different heat exchangers flow patterns. Liquid height at atmospheric pressure.
Non-Regenerative Heat Exchanger The non-regenerative application is the most frequent and involves two separate fluids. In thermodynamics heat is energy in transfer to or from a thermodynamic system by mechanisms other than thermodynamic work or transfer of matter eg. On the top of the heat exchanger.
Like thermodynamic work heat transfer involves the surroundings of a system as well as the system itself and so is not a property of the system alone though it contributes to. The double pipe heat exchanger is one heat exchanger pipe inside another larger pipe for either counter flow or parallel flow pattern. Effectiveness NTU Method ε NTU.
The engine oil at a flow rate of 023 kgs enters the exchanger at 120C and leaves at 115C. Get 247 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. Conduction radiation and friction.
Model Equations and Heuristics. Q U A F LMTD. The primary and secondary fluid in an heat exchanger process may.
The general function of a heat exchanger is to transfer heat from one fluid to another. 𝑙𝑙𝑚𝑚 𝐹𝐹 𝑇𝑇. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact.
Each has an associated heat transfer coefficient cross-sectional area for heat transfer and temperature difference. They are widely used in space heating refrigeration air conditioning power stations chemical plants petrochemical plants. 𝑃𝑃where 𝐹𝐹 is a correction factor obtained from the figures by calculating P R values.
Flow in the same direction - parallel flow or co-current flow. In the following some of these classes and the related equations are presented. 100 of the flow cross-section in the evaporator.
The mean temperature difference in a heat transfer process depends on the direction of fluid flows involved in the process.

Calculating Rate Of Heat Transfer In Parallel Flow Heat Exchangers Youtube

Chapter 3 2 Heat Exchanger Analysis Using Ntu Method Ppt Video Online Download
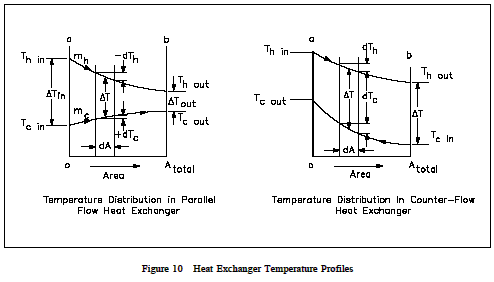
Parallel And Counter Flow Designs Heat Exchangers

Understanding Heat Exchangers Types Designs Applications And Selection Guide

0 Response to "Cross Flow Heat Exchanger Equations"
Post a Comment